Data wrangling & manipulation in R - workshop site
Day 2 notes: Manipulating your data & an intro to dplyr
Ruan van Mazijk
A note on base vs tidyverse R data manipulation
data[, columns]
data[rows, ]
data[, 4]
data[, "plantheight"]
data[1:10, ]
data[data$soil == "a", ]
Compare these to the tidyverse-equivalents, from dplyr:
data %>%
select(plantheight)
data %>%
filter(soil == "a")
dplyr
Verbs to manipulate your data
select() # operates on columns
filter() # operates on rows
Examples
data %>%
select(...)
# These do the same thing:
data %>%
select(plant_height, soil, lon, lat, veg_type)
data %>%
select(plant_height:veg_type)
# Think 1:10 but with words!
data %>%
select(-mean_annual_temp)
# Think data[, -10],
# Or like gather(key, value, -foo)
# These do the same thing:
data %>%
select(plant_height, plant_weight, plant_LAI)
data %>%
select(starts_with("plant"))
# See also:
# contains() ends_with() matches()
# num_range() one_of() starts_with()
# We can also select() all columns that satisfy a predicate:
data %>%
select_if(is.numeric)
# Accepts base R functions (sans "()"):
# is.logical is.character is.numeric
# is.factor is.datetime
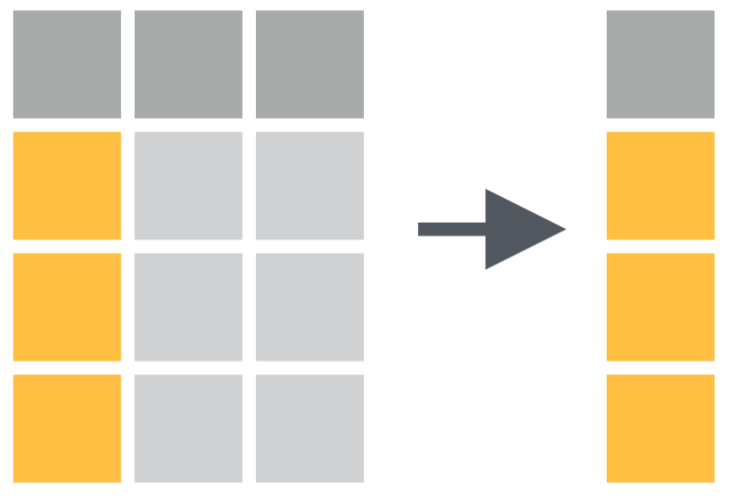
data %>%
filter(...)
data %>%
filter(plant_height <= 10)
data %>%
filter(plant_height <= 10, vegtype == "fynbos")
# Multiple conditions must all be satisfied
# So it "&"s them, so it would be the same as:
data %>%
filter(plant_height <= 10 & vegtype == "fynbos")
# We can use "or" with the "|" operator:
data %>%
filter(plant_height <= 10 | plant_weight >= 60)
# Intervals?
data %>%
filter(plant_height <= 10 & plant_height >= 0.5)
# There is also a tidy way!
data %>%
filter(plant_height %>% between(0.5, 10))
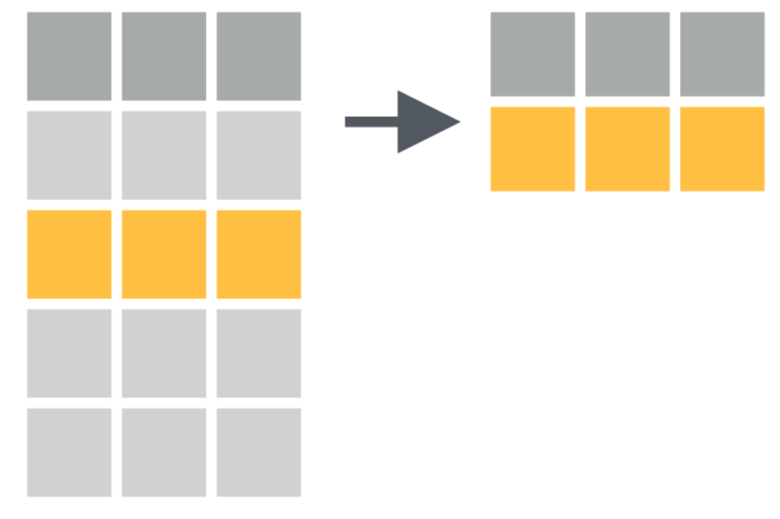
Diagrams illustrating gather(), spread(), separate() and unite() are taken from RStudio cheatsheets (CC BY SA RStudio)